
Corporate banking companies and investment banking companies offer unique financial services that help businesses and governments with their financial needs. They differ in several ways, including their purpose, service focus, education, training, career prospects, functions, and target clients. It is better to understand corporate banking vs investment banking for those who want to make a career in finance because each path leads to distinct opportunities, challenges, and skill requirements.
Table of Contents:
- Corporate Banking vs Investment Banking: A Comprehensive Overview
- Key Differences between Corporate Banking and Investment Banking
- Services offered by Corporate vs Investment Banking
- Prerequisites of Corporate Banking vs Investment Banking
- Corporate Banking Vs Investment Banking Salary
- Corporate vs Investment Banking: Better Career Option
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
A Comprehensive Overview of Corporate Banking vs Investment Banking
Corporate Banking vs Investment Banking are major career paths often considered by individuals who aspire to become finance professionals. No doubt, both of them fulfill the financial needs of business organizations but they have distinct ways to do so. So, first, let us get to understand what is corporate banking and what is investment banking.
What is Corporate Banking?
The term, corporate banking hints at what is corporate banking. It is basically one of the aspects of banking that are known to provide financial services to large businesses, corporations, and institutions. These financial services primarily deal with routine financial services for businesses. Corporate banking provides various services including lending & credit facilities, trade finance, treasury & cash management, corporate advisory, and risk management solutions.
Corporate banking companies serve SMEs (small & medium-scale enterprises) to large multinational companies. These clients seek comprehensive financial solutions for their operational and strategic needs which is why corporate banking is essential for businesses looking to optimize their financial health, manage risk, and achieve long-term growth.
Corporate banking professionals generally have to build long-term relationships with their clients, to provide consistent support and customized solutions that align with the client’s progressive financial needs.
What is Investment Banking?
Investment banking focuses on helping companies, governments, and other entities. Investment bankers help raise capital and execute complex financial transactions between investors and corporations. The professionals provide underwriting, issuance of new securities, mergers & acquisitions, and IPO management services to its clients.
Investment banks are intermediates between large corporations, governments, private equity firms, hedge funds, high-net-worth individuals, and investors when the company wants to issue stock or bonds. These clients seek strategic advice for capital raising, strategic planning, and guidance on significant transactions that have the potential to drive growth, expansion, and restructuring, and have the potential to shape their future growth.
Investment banking companies are fast-paced, offering a high-stakes environment to work. Professionals develop deep expertise in financial markets, deal-making, and regulatory compliance in these Investment banking companies. The focus is on delivering high-value transactions and maximizing returns, often requiring a strong foundation in analytical skills, financial modelling, and negotiation.
Now that we have explored what is corporate banking and what is investment banking. Let us know the key differences between these two fields. Explore what makes each of them unique which will help clarify which career path will be the best fit for you based on your skills, interests, and career aspirations.
Key Differences between Corporate Banking and Investment Banking
Both corporate banking companies and investment banking companies operate within the financial sector but they have different functions, clients, and purposes. So, take a look at the table below to easily understand the differences of both fields side-by-side.
| Corporate Banking Companies and Investment Banking Companies | ||
| Feature | Corporate Banking | Investment Banking |
Focus and Scope of Services | Provides loans, credit, treasury management, trade finance, and other routine services for businesses. | Focuses on capital raising, mergers and acquisitions (M&A), underwriting, and strategic financial advisory. |
Client Relationships | Long-term, relationship-based services with stable clients. | Transactional and deal-focused relationships are often linked to specific financial events. |
Work Environment | A stable, predictable work environment with regular hours; emphasis on client service and relationship management. | A fast-paced, high-pressure environment with long hours; focus on financial modeling, deal-making, and client interaction. |
Skills | Strong analytical and relationship management skills; | Advanced financial modeling, valuation, and negotiation skills; |
Qualifications | degrees in finance or business; CFA/CA preferred | MBA background preferred in finance, economics |
Career Progression | Linear career paths (e.g., Relationship Manager to Corporate Banker) | Structured career path (e.g., Analyst to Managing Director) |
Types of Clients | SMEs and large corporations | Large corporations, governments, private equity firms, hedge funds, and high-net-worth individuals |
Regulatory Environment | lending practices and risk management | securities, capital markets, and underwriting activities. |
Services Offered by Corporate vs Investment Banking
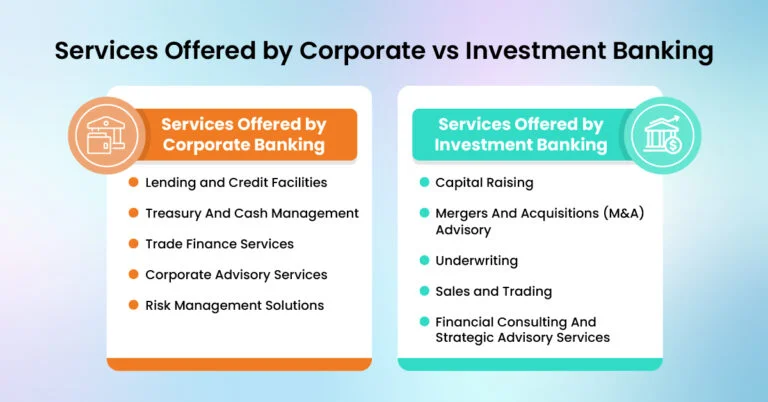
It is essential to explore the specific services provided by corporate banks vs investment banks to understand their unique roles as they serve different client needs and financial activities.
Services Offered by Corporate Banking
Corporate banks offer a range of services to help businesses manage their financial needs and operations, which include:
Lending and Credit Facilities
Corporate banks provide various types of loans including working capital loans, term loans, revolving credit lines, and syndicated loans to help businesses manage their cash flow, finance capital expenditures, and fund specific projects. They maintain long-term relationships with their clients and customize credit solutions that align with their client’s growth and operational needs.
Treasury And Cash Management
Corporate banks also provide cash concentration, disbursement services, automated clearing house (ACH) transactions, and foreign exchange management services crucial for the efficient financial management of businesses.
Trade Finance Services
Corporate banks provide services like letters of credit, export financing, guarantees, and supply chain finance to support businesses engaged in international trade. These services help companies manage risks and ensure smooth cross-border transactions.
Corporate Advisory Services
Corporate advisory services offered by corporate banks include financial structure optimization, debt management, and regulatory compliance to advise small-scale mergers or acquisitions, but not in detail as investment banks do.
Risk Management Solutions
Corporate banks help clients reduce financial risks related to interest rate fluctuations, currency exchange rate changes, and commodity price changes. They use interest rate swaps, currency swaps, and commodity derivatives to mitigate financial risks. However, they generally take less risk in complex capital market transactions. They focus on providing steady support for their clients’ operational financial needs.
Services Offered by Investment Banking
Investment Bankers offer a range of specialized financial services to facilitate large-scale transactions, raise capital, and deliver strategic financial advisory.
Capital Raising
Investment banks help clients gain funds which also includes orchestrating initial public offerings (IPOs), secondary offerings, and private placements so that companies can access capital markets and attract investors.
Mergers And Acquisitions (M&A) Advisory
Investment banks identify potential acquisition targets or buyers, negotiate terms, structure deals, and manage the entire transaction process.
Underwriting
Investment banks also act as intermediaries between issuers of securities and the investing public. They purchase securities from the issuer and sell them to investors by assuming the risk of the sale.
Sales and Trading
Investment banks buy and sell securities sometimes on behalf of their clients, including equities, bonds, and derivatives. It helps manage risk and provides clients with access to diverse investment opportunities.
Financial Consulting And Strategic Advisory Services
Investment banks guide financial restructuring, valuation, capital optimization, and market positioning in complex transactions or high-value deals. They are experts in navigating challenging financial decisions, enhancing their ability to achieve long-term strategic objectives.
Prerequisites of Corporate Banking vs Investment Banking
To build a successful career in corporate banking, you must meet educational qualifications, technical expertise, industry knowledge, and essential interpersonal skills.
No doubt for the prerequisites of corporate banking, educational background must be in relevant fields of study like finance, business administration, accounting, or economics. It is not necessary to have an MBA but advanced certifications like Chartered Accountant (CA) or Certified Treasury Professional (CTP) can enhance your profile. Understanding of corporate finance, credit analysis, lending practices, and banking regulations, with proficiency in financial analysis, credit risk assessment, and the ability to interpret financial statements help you stand out in the crowd. Along with that, strong communication skills help in managing client interactions and providing customized banking solutions. Lastly, experience as a credit analyst, relationship manager, or loan officer, or internships in commercial or corporate banks, lays a valuable foundation for aspiring corporate bankers.
However, Investment banks prefer candidates having strong academic backgrounds, especially MBAs or CFAs. They expect these professionals to be technically sound in financial modeling, valuation techniques, and advanced Excel. Possessing strong analytical and quantitative skills helps them handle large and complex financial data. Moreover, investment bankers need to be good at communication so that they can build and maintain client relationships and navigate complex transactions. If you’re wondering how to become an investment banker, mastering both analytical and communication skills is vital for navigating complex deals and building client trustSo, candidates with prior relevant internships or work experience as a financial analyst or equity researcher can easily secure a position in investment banking.
Corporate Banking Vs Investment Banking Salary
Consider the salary aspect if you are thinking of building a career in finance. Both corporate banking vs investment banking salary packages are attractive but you may notice significant differences in pay scales, bonus structures, and earning potential across different levels of experience. So, here is an overview of the Corporate Banker vs Investment Banker salary ranges.
Corporate Banking Vs Investment Banking Salary | ||
Position | Corporate Banker Salary | Investment Banker Salary |
Entry-Level | $60,000 – $80,000 | $85,000 – $125,000 |
Mid-Level | $80,000 – $120,000 | $150,000 – $300,000 |
Senior Level | $120,000 – $250,000+ | $300,000 – $1,000,000+ |
Bonuses | Performance-based | Performance-based |
Overall Compensation | stable and consistent | Higher base salaries |
The corporate banker salary is stable and their bonuses are performance-based but smaller. Investment Banker salary are higher than corporate banker salary and huge bonuses increase their total earnings. It is a highly demanding job that may have more than 12 working hours irrespective of corporate banking. The salary packages generally vary depending on experience, location, and the size of the institution.
Curious about the salary after an investment banking course? Watch this video to find out.
Corporate vs Investment Banking: Better Career Option
Both careers cater to different strengths and aspirations. It’s important to consider some of the trade-offs between stability and high rewards to make an informed decision that aligns with your professional and personal goals.

Corporate Banking Career
If you aspire to have a stable career, then working in the corporate banking sector is the right choice. Maintaining long-term relationships and working with businesses to meet their financial needs constitutes their job responsibility. They enjoy a balanced lifestyle with less intensive working hours.
Moreover, a structured career progression offers clear pathways from entry-level positions to senior roles like relationship managers, credit officers, and senior management. Corporate bankers earn competitive salary packages with comprehensive bonuses. So, work-life balance and lower stress levels make corporate banking a suitable job for those who want a more sustainable option for the long term.
Investment Banking Career
Investment banking jobs offer high financial rewards but do consider that the higher the salary, the bigger the responsibility. It is a fast-paced, high-stakes work involving mergers and acquisitions (M&A), capital raising, underwriting, and strategic advisory. Investment bankers work for longer hours, especially in junior positions but there is potential for rapid career growth.
Moreover, the financial compensation includes a high base salary and a large performance bonus, making it a lucrative job for many.
This dynamic career path offers opportunities to quickly advance to roles like associate, vice president, director, and managing director. The skills acquired in investment banking—such as financial modeling, valuation, and deal negotiation—are highly transferable which opens doors to a range of other finance-related careers, like private equity, hedge funds, and corporate strategy.
Therefore, the better career option between corporate banking and investment banking ultimately depends on your personal preferences, skills, and career goals. If you value a balanced lifestyle and a steady career with growth opportunities, corporate banking may be the better choice. But if you are driven by high financial rewards, investment banking could be the more suitable path.
Conclusion
Both Corporate vs Investment Banking are integral parts of the financial sector, offering unique career opportunities. Choosing between both career paths is tough but if you want a long-term career then go for corporate banking. If you seek a career with a higher potential to earn, investment banking may be your right choice. So decide on your preferences and choose the right career trajectory as it will impact all your life.
FAQ’s
Is investment banking part of corporate banking?
No, both are integral segments of the financial domain. So neither of them is part of the other. These both are different.
What are the types of investment banking?
There are three types namely - bulge bracket banks, middle-market banks, and boutique banks. These banks often include regional boutiques and elite boutique banks each serving different market segments and specializing in various financial services.
What is the main function of an investment bank?
Investment banks primarily help businesses and governments to meet their daily financial needs. Investment banks act as middlemen between investors and issuers to help clients raise money.
What qualifications do I need to become an investment banker?
It is a must to have a bachelor’s degree. Strong analytical and quantitative skills and a deep understanding of financial markets are also necessary to pass licensing exams.









